Multi Arm Bandit Problem
Contents
Multi Arm Bandit Problem#
Introduction#
Row of slot machines with different probabilities of paying off? Which ones should you play often and how often?
Exploit vs Explore
Application Areas
Model for A/B Testing: Ad someone clicks or doesnot
Medical Diagnosis: Well known treatment or new treatment
Diseases Epidemic :
import numpy as np
import scipy as sp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import empiricaldist
from empiricaldist import Pmf, Distribution
from ipywidgets import interact, interactive, fixed
Prior#
def decorate_bandit(title):
"""
Labels the axes
title: string
"""
plt.xlabel('Probability of winning')
plt.ylabel('PMF')
plt.title(title)
bandit = Pmf.from_seq(range(101))
bandit.plot()
decorate_bandit(title="Prior Distribution")

We are assuming uniform prior distribution here for probability
def likelihood_bandit(data, hypo):
x = hypo/100
if data == "W":
return x
else:
return 1-x
actual_probs = [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4]
def posterior(n_w=1, n_l=9):
bandit = Pmf.from_seq(range(101))
outcomes = 'W'*n_w+"L"*n_l
bandit.plot(color='steelblue', label='Prior', linestyle="--")
for data in outcomes:
bandit.update(likelihood_bandit, data)
bandit.plot(color='steelblue', label='Posterior')
plt.legend()
decorate_bandit(title="Prior vs Posterior")
interactive(posterior, n_w=(0,10), n_l=(0,10))
Simulate Machines Based on Given Probabilities#
from random import random
from collections import Counter
counter = Counter()
def flip(p):
return random()<p
def play(i):
counter[i] += 1
p = actual_probs[i]
if flip(p):
return 'W'
else:
return 'L'
play(1), play(2), play(3), play(0)
('W', 'L', 'W', 'W')
Playing machines 20 times#
results = []
for i in range(20):
single = []
for j in range(4):
# print(i,j)
single.append(play(j))
results.append(single)
counter[4]
0
list(range(4))
[0, 1, 2, 3]
results
[['L', 'L', 'L', 'L'],
['L', 'W', 'L', 'W'],
['L', 'W', 'L', 'L'],
['L', 'W', 'W', 'L'],
['L', 'W', 'L', 'W'],
['L', 'L', 'L', 'L'],
['L', 'L', 'W', 'L'],
['L', 'W', 'W', 'L'],
['L', 'L', 'L', 'W'],
['W', 'W', 'L', 'L'],
['L', 'L', 'L', 'L'],
['L', 'L', 'W', 'L'],
['W', 'W', 'W', 'L'],
['L', 'W', 'L', 'L'],
['L', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['L', 'W', 'L', 'W'],
['L', 'W', 'W', 'L'],
['W', 'L', 'L', 'L'],
['L', 'L', 'L', 'L'],
['L', 'L', 'L', 'L']]
prior = range(101)
beliefs = [Pmf.from_seq(prior) for i in range(4)]
beliefs
[0 0.009901
1 0.009901
2 0.009901
3 0.009901
4 0.009901
...
96 0.009901
97 0.009901
98 0.009901
99 0.009901
100 0.009901
Length: 101, dtype: float64,
0 0.009901
1 0.009901
2 0.009901
3 0.009901
4 0.009901
...
96 0.009901
97 0.009901
98 0.009901
99 0.009901
100 0.009901
Length: 101, dtype: float64,
0 0.009901
1 0.009901
2 0.009901
3 0.009901
4 0.009901
...
96 0.009901
97 0.009901
98 0.009901
99 0.009901
100 0.009901
Length: 101, dtype: float64,
0 0.009901
1 0.009901
2 0.009901
3 0.009901
4 0.009901
...
96 0.009901
97 0.009901
98 0.009901
99 0.009901
100 0.009901
Length: 101, dtype: float64]
options = dict(xticklabels='invisible', yticklabels='invisible')
def plot(beliefs,label_pre='Prior',**options):
sns.set_context('paper')
for i, b in enumerate(beliefs):
plt.subplot(2,2, i+1, label=f"{label_pre}{i}")
b.plot(label=f"Machine {i}")
plt.gca().set_yticklabels([])
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
sns.set_context('talk')
plot(beliefs)
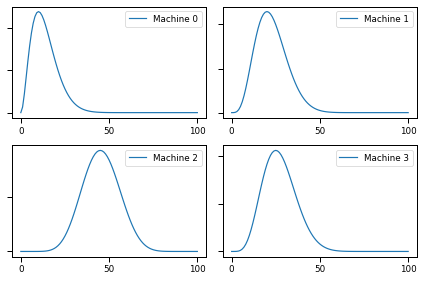
def update(beliefs, i, outcome):
beliefs[i].update(likelihood_bandit, outcome)
prior = range(101)
counter = Counter()
def flip(p):
return random()<p
def play(i):
counter[i] += 1
p = actual_probs[i]
if flip(p):
return 'W'
else:
return 'L'
def update(beliefs, i, outcome):
beliefs[i].update(likelihood_bandit, outcome)
beliefs = [Pmf.from_seq(prior) for i in range(4)]
# beliefs
plot(beliefs, label_pre='Prior')
for i in range(20):
for j in range(4):
update(beliefs, j, play(j))
plot(beliefs, label_pre='Posterior')
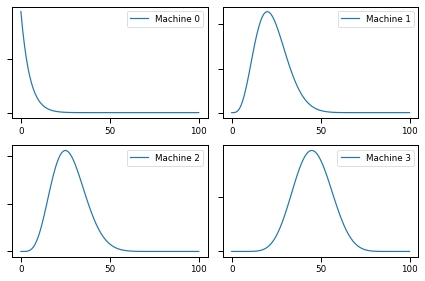
for i, b in enumerate(beliefs):
print(f"{b.mean():0.02f}", b.credible_interval(0.9))
9.12 [ 2. 21.]
22.73 [10. 38.]
50.00 [33. 67.]
27.27 [13. 44.]
Bayesian Bandit#
Idea is to choose best course of action while running the experiment/ simulation
Choice internally call np.random.choice on quantities
# def choose(beliefs):
# ps = []
beliefs[3].choice()
40
# Pmf.choice?
beliefs[3].qs
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12,
13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25,
26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38,
39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51,
52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64,
65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77,
78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90,
91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100])
ps = [b.choice() for b in beliefs]
ps, np.argmax(ps)
([0, 11, 21, 40], 3)
def choose(beliefs):
ps = [b.choice() for b in beliefs]
return np.argmax(ps)
choose(beliefs)
3
def choose_play_update(beliefs, verbose=False):
machine = choose(beliefs)
outcome = play(machine)
update(beliefs,machine,outcome)
if verbose:
print(machine, outcome, beliefs[machine].mean())
choose_play_update(beliefs, verbose=True)
3 W 42.85714285714286
prior = range(101)
beliefs = [Pmf.from_seq(prior) for i in range(4)]
counter = Counter()
num_plays = 200
for i in range(num_plays):
choose_play_update(beliefs)
plot(beliefs)
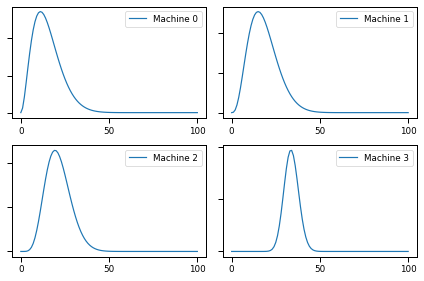
for i,b in enumerate(beliefs):
print(b.mean(), b.credible_interval(0.9))
15.000082130288831 [ 4. 30.]
18.181782304462693 [ 7. 33.]
21.2121212181695 [11. 34.]
33.834586466165426 [27. 41.]
for machine, count in sorted(counter.items()):
print(machine , count)
0 18
1 20
2 31
3 131


